📚 Overview
What is WebRTC?
WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication) is a technology that enables peer-to-peer communication between browsers and mobile applications. It allows real-time audio, video, and data exchange without requiring plugins or additional software.
Key Components
- STUN Server: Discovers public IP addresses for direct peer-to-peer connections
- TURN Server: Relays media traffic when direct connections fail (4G, firewalls, NAT)
- Signaling: WebSocket-based event exchange for connection setup
- ICE (Interactive Connectivity Establishment): Framework for finding the best connection path
Architecture
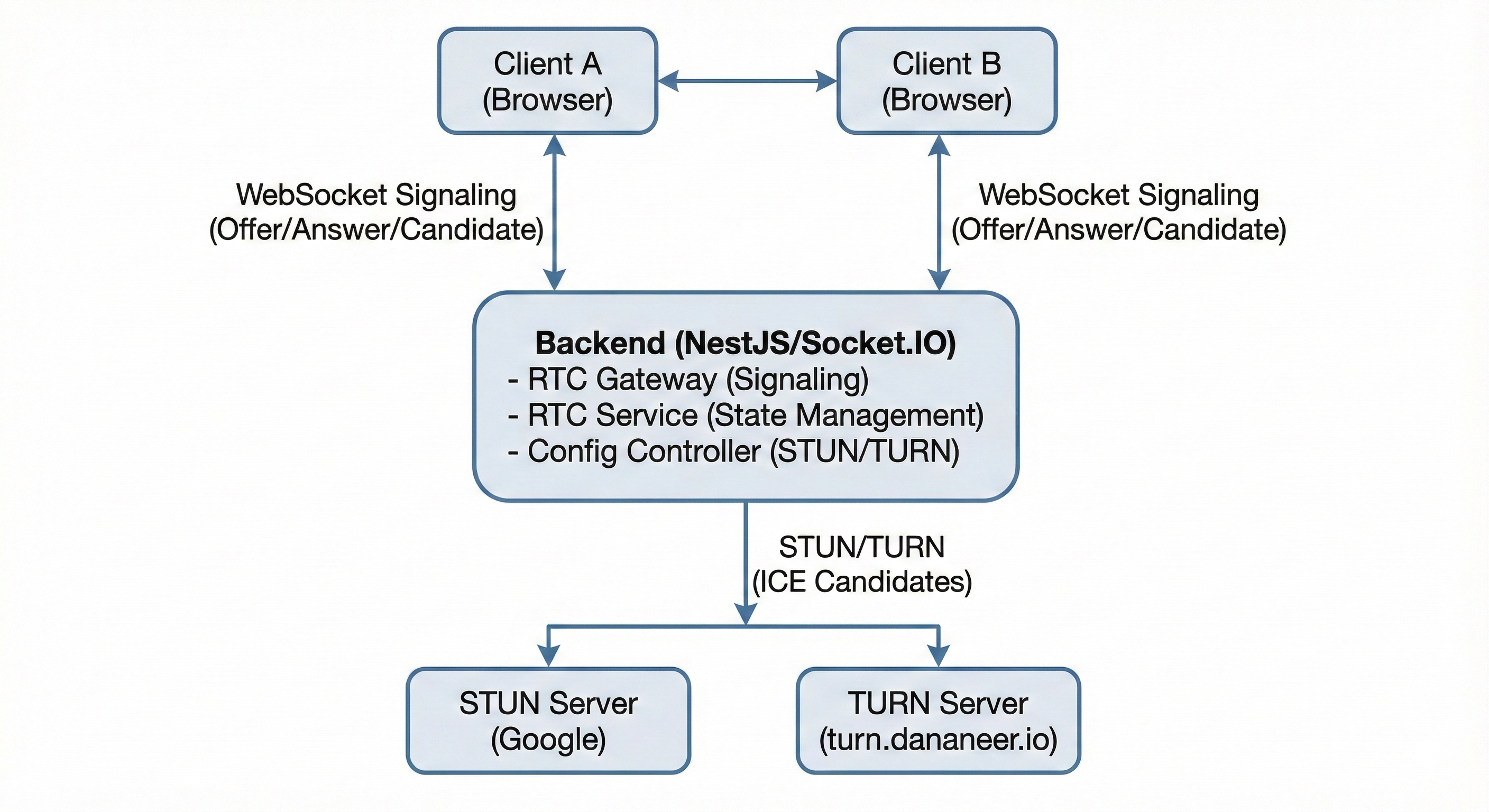
🔄 Call Lifecycle
Join/Start Call
User initiates or joins a call by emitting rtc:joinCall with callId and optional initial media state. Backend creates the call room if it doesn't exist and adds the user as a participant. If other participants exist, they receive rtc:participantJoined event.
Call Started Event
After joining, the client receives rtc:callStarted event with the callId and list of all current participants. This allows the client to synchronize with existing participants.
ICE Configuration
Clients fetch RTC configuration via GET /api/v1/rtc/config to get STUN/TURN servers and create RTCPeerConnection (Web) or PeerConnection (Unity) with ICE servers.
Create Offer
Caller creates an offer using createOffer() and sets it as local description. The SDP is sent via rtc:offer event to the target user.
Receive Offer & Create Answer
Receiver sets the offer as remote description, creates an answer with createAnswer(), sets it as local description, and sends it via rtc:answer event.
ICE Candidate Exchange
As ICE candidates are discovered, they are exchanged via rtc:candidate events. This continues until a connection is established or all candidates are exhausted.
Connection Established
When ICE connection state becomes connected, media streams flow directly between peers (or via TURN relay if needed).
Media State Updates
Participants can toggle audio/video/screen sharing via rtc:toggleMute, rtc:toggleVideo, rtc:toggleScreenShare. Changes are broadcast via rtc:mediaUpdated.
Leave Call
User emits rtc:leaveCall or disconnects. Backend removes them from the room and broadcasts rtc:participantLeft to remaining participants. When the last participant leaves, the room is automatically cleaned up.
📡 Events Reference
Client → Server Events (Subscribed)
| Event | Payload | Description |
|---|---|---|
rtc:ping |
{} |
Ping server, receive pong with config |
rtc:joinCall |
{ callId, initialMediaState? } |
Join or start a call (idempotent - creates call if doesn't exist) |
rtc:leaveCall |
{ callId } |
Leave the current call |
rtc:offer |
{ callId, toUserId, sdp } |
Send WebRTC offer SDP |
rtc:answer |
{ callId, toUserId, sdp } |
Send WebRTC answer SDP |
rtc:candidate |
{ callId, toUserId, candidate } |
Send ICE candidate |
rtc:toggleMute |
{ callId, muted } |
Toggle audio mute state |
rtc:toggleVideo |
{ callId, enabled } |
Toggle video enabled state |
rtc:toggleScreenShare |
{ callId, enabled } |
Toggle screen sharing |
Server → Client Events (Published)
| Event | Payload | Description |
|---|---|---|
rtc:pong |
{ ts, rtc: { maxParticipants }, echo } |
Response to ping |
rtc:callStarted |
{ callId, participants } |
Call started, includes all participants |
rtc:participantJoined |
{ callId, userId, mediaState } |
New participant joined |
rtc:participantLeft |
{ callId, userId } |
Participant left the call |
rtc:offer |
{ callId, fromUserId, toUserId, sdp } |
Relayed offer from another participant |
rtc:answer |
{ callId, fromUserId, toUserId, sdp } |
Relayed answer from another participant |
rtc:candidate |
{ callId, fromUserId, toUserId, candidate } |
Relayed ICE candidate |
rtc:mediaUpdated |
{ callId, userId, mediaState } |
Participant media state changed |
rtc:error |
{ code, message, details? } |
Error occurred |
⚙️ Configuration
Backend Environment Variables
RTC_STUN_URLS Optional
STUN server URLs (comma-separated). Defaults to Google STUN servers if not set.
RTC_STUN_URLS=stun:stun.l.google.com:19302,stun:stun1.l.google.com:19302
RTC_TURN_URLS Optional
TURN server URLs with transport types. Required for 4G/5G networks.
RTC_TURN_URLS=turn:turn.dananeer.io:3478?transport=udp,turn:turn.dananeer.io:3478?transport=tcp,turns:turn.dananeer.io:443?transport=tcp
RTC_TURN_USERNAME Required
TURN server username. Required if TURN_URLS is set.
RTC_TURN_USERNAME=dananeer_turn
RTC_TURN_CREDENTIAL Required
TURN server password. Required if TURN_URLS is set.
RTC_TURN_CREDENTIAL=rZBSJ0z2mrDU4ja6j9DT5yPG
RTC_MAX_PARTICIPANTS Optional
Maximum participants per call. Default: 4, Range: 2-10.
RTC_MAX_PARTICIPANTS=4
Network Support
✅ LAN Networks
UDP transport (fastest)
✅ WiFi Networks
UDP/TCP transport
✅ 4G/LTE Networks
TLS transport (port 443)
✅ 5G Networks
TLS transport (port 443)
✅ Firewalls
TLS transport (port 443)
✅ Symmetric NAT
TURN relay
✅ Corporate Networks
TLS transport (port 443)
🔌 API Reference
Get RTC Configuration
Retrieve STUN/TURN server configuration for WebRTC peer connections.
GET /api/v1/rtc/config
Headers:
Authorization: Bearer <access_token>
Response: 200 OK
{
"turnUrls": [
"turn:turn.dananeer.io:3478?transport=udp",
"turn:turn.dananeer.io:3478?transport=tcp",
"turns:turn.dananeer.io:443?transport=tcp"
],
"turnUsername": "dananeer_turn",
"turnCredential": "rZBSJ0z2mrDU4ja6j9DT5yPG",
"stunUrls": [
"stun:stun.l.google.com:19302",
"stun:stun1.l.google.com:19302"
],
"maxParticipants": 4
}
💻 Integration Guide
Web Frontend Implementation
1. Fetch RTC Configuration
async function fetchRtcConfig() {
const response = await fetch('/api/v1/rtc/config', {
headers: {
'Authorization': `Bearer ${accessToken}`
}
});
return await response.json();
}
2. Initialize RTCPeerConnection
const config = await fetchRtcConfig();
const iceServers = [
...config.stunUrls.map(url => ({ urls: url })),
...config.turnUrls.map(url => ({
urls: url,
username: config.turnUsername,
credential: config.turnCredential
}))
];
const pc = new RTCPeerConnection({ iceServers });
3. Handle ICE Candidates
pc.onicecandidate = (event) => {
if (event.candidate) {
socket.emit('rtc:candidate', {
callId: currentCallId,
toUserId: targetUserId,
candidate: event.candidate
});
}
};
4. Handle Offer/Answer
socket.on('rtc:offer', async (data) => {
await pc.setRemoteDescription(
new RTCSessionDescription({ type: 'offer', sdp: data.sdp })
);
const answer = await pc.createAnswer();
await pc.setLocalDescription(answer);
socket.emit('rtc:answer', {
callId: data.callId,
toUserId: data.fromUserId,
sdp: pc.localDescription.sdp
});
});
socket.on('rtc:answer', async (data) => {
await pc.setRemoteDescription(
new RTCSessionDescription({ type: 'answer', sdp: data.sdp })
);
});
5. Handle Media Streams
pc.ontrack = (event) => {
const remoteStream = event.streams[0];
remoteVideoElement.srcObject = remoteStream;
};
navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia({ audio: true, video: true })
.then(stream => {
localVideoElement.srcObject = stream;
stream.getTracks().forEach(track => {
pc.addTrack(track, stream);
});
});
🎮 Unity Integration
Overview
Unity applications can integrate with the WebRTC backend using Socket.IO client libraries and Unity's WebRTC package. The backend API is platform-agnostic and works with any WebRTC-compatible client.
Required Packages
Unity WebRTC package is available through Unity Package Manager. You'll also need a Socket.IO client library compatible with Unity (C#) for WebSocket signaling. Popular options include SocketIOClient or similar C# Socket.IO implementations.
Platform Support
Unity WebRTC supports multiple platforms including Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android. This makes it ideal for cross-platform game development with voice communication features.
Integration Steps
- Install Unity WebRTC Package: Add the Unity WebRTC package through Package Manager using the Git URL or Unity Registry.
- Add Socket.IO Client: Integrate a Socket.IO client library for C# to handle WebSocket signaling with the backend.
- Fetch RTC Configuration: Make an HTTP GET request to
/api/v1/rtc/configendpoint with your access token to retrieve STUN/TURN server configuration. - Initialize PeerConnection: Create a Unity WebRTC PeerConnection instance with the ICE servers from the configuration response.
- Connect Socket.IO: Establish WebSocket connection to the backend with JWT token for authentication.
- Join Call: Emit
rtc:joinCallevent with the callId to join or start a call. - Handle Signaling: Listen for
rtc:offer,rtc:answer, andrtc:candidateevents and process them with Unity WebRTC APIs. - Add Audio Track: Capture audio from Unity's audio system and add it to the peer connection.
- Handle Remote Audio: Receive remote audio tracks and route them to Unity's audio playback system.
- Manage Lifecycle: Handle call lifecycle events (
rtc:callStarted,rtc:participantJoined,rtc:participantLeft) and update your game UI accordingly.
Key Considerations for Unity
- Threading: WebRTC operations in Unity run on background threads. Ensure UI updates happen on Unity's main thread.
- Audio Handling: Use Unity's AudioSource components for playback and Unity WebRTC's audio capture APIs for microphone input.
- Permissions: Request microphone permissions on mobile platforms (Android/iOS) before attempting to capture audio.
- Network Configuration: Ensure TURN servers with TLS transport are configured for mobile networks (4G/5G) to work reliably.
- Event Handling: Socket.IO events should be processed asynchronously and integrated with Unity's event system.
- Error Handling: Implement proper error handling for network failures, ICE connection failures, and authentication errors.
- State Management: Track call state, participant lists, and media state changes to keep your game synchronized.
Backend Compatibility
The backend WebRTC API is fully compatible with Unity clients. All events, payloads, and lifecycle management work identically whether connecting from a web browser or Unity application. The only difference is the WebRTC implementation library used on the client side.
Testing Unity Integration
When testing Unity integration, ensure you test on the target platforms (especially mobile) as WebRTC behavior can vary between platforms. Test with different network conditions including WiFi, 4G, and 5G to verify TURN server configuration is working correctly.
🔧 Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Connection Fails on 4G Network
Problem: WebRTC connection fails on mobile 4G networks.
Solution: Ensure TURN servers with TLS transport are configured:
RTC_TURN_URLS=turns:turn.dananeer.io:443?transport=tcp
No Audio/Video
Problem: Connection established but no media streams.
Solution: Check that tracks are added to peer connection and remote stream handlers are set up correctly.
ICE Connection Stuck on "checking"
Problem: ICE connection state remains "checking" indefinitely.
Solution: Verify STUN/TURN servers are accessible and credentials are correct. Check browser console for ICE candidate errors.
High Latency
Problem: High latency in media streams.
Solution: Check if TURN relay is being used (check ICE connection type). For LAN/WiFi, ensure UDP transport is prioritized.
Debugging
pc.oniceconnectionstatechange = () => {
console.log('ICE Connection State:', pc.iceConnectionState);
};
pc.onconnectionstatechange = () => {
console.log('Connection State:', pc.connectionState);
};
pc.onicegatheringstatechange = () => {
console.log('ICE Gathering State:', pc.iceGatheringState);
};